“In the role-playing activity Starving Artist, for example, groups of students are encouraged to come up with an idea for a musical act, write lyrics and design a CD cover only to be told by a volunteer teacher their work can be downloaded free. According to the lesson, the volunteer would then “ask them how they felt when they realized that their work was stolen and that they would not get anything for their efforts.” NY Times, Sep 25, 2003
What is hilarious about this little scenario, of course, is that it is a complete fantasy. It is a comic fantasy. The most hilarious part is where they convince the students that they would actually have received any of the money that should have been paid for the CDs.
A real world scenario would run thusly: the students come up with an idea for a musical act, write lyrics and music and create a CD cover, and get signed by a major record label.
While in the recording studio, the producer, assigned by the record label, makes some suggestions for the arrangement of their best songs. Then, of course, he convinces them to give him a co-writing credit.
Their CD sells very well because it is played on the radio– for free– and they perform on television promoting the CD– for free. They have a big advance from the record company and sign a complicated contract they don’t understand. They spend all their money in one year.
The next year, their accountants –played by a volunteer teacher, if you will– tell them they are broke.
They find out that the record company has been deducting all the expenses of recording, packaging, shipping, and promoting their CD against all their royalties. They find out that a whopping bill came from an image consultant hired by the record company on their behalf and at their expense. Then they find out that the image consultant actually works for the record company for a pittance. They find out that the image consultant, sound engineer, label designer, photographer, and graphic artist all did the same work for several other artists signed to the same record label but who didn’t sell very many CDs at all.
They find out that they owe the record company millions of dollars. They find out that the producer has collected a huge chunk of their song-writing royalties.
They write and compose a follow-up CD. This time, the producer brings in a “rhythm consultant” who also takes a co-writing credit. A record company executive doesn’t like it and demands changes. He wants it to be more pop, less art. The students don’t like the changes at all and demand artistic freedom. The record company tells them that they must change their music or they will not be allowed to release the record. Nor will they be released from their contract and allowed to switch labels to work with a producer who understands what they are trying to do.
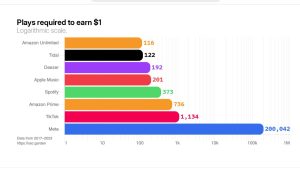
Their CD is released on Spotify. It is downloaded 100,000 times. They receive a payment from Spotify of $12.53.
They find out that their work was stolen and they would not get anything for their efforts.
Now they know what it feels like to have their hard work stolen from them.
You may now resume downloading.